A Silent Crisis Unfolding in India
India is currently facing a silent yet devastating health crisis—an alarming rise in impotency and infertility among its population. Once considered a problem of the modern, urban elite, reproductive health issues are now affecting people across all demographics, including rural communities. The situation has reached a point where experts are sounding the alarm, calling it a national emergency that demands immediate attention.
The Startling Statistics
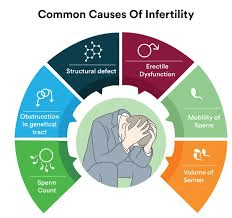
According to recent studies, nearly 27.5 million couples in India suffer from infertility, and the numbers are increasing at an alarming rate. Male infertility, which was once overshadowed by female reproductive issues, now accounts for 40-50% of infertility cases. Simultaneously, an increasing number of young men are reporting erectile dysfunction (ED), with nearly 15-20% of men under 40 experiencing some form of impotency. Additionally, studies indicate that India’s total fertility rate (TFR) has dropped below the replacement level of 2.1 children per woman, raising concerns about future demographic shifts.
What is Causing This Epidemic?
1. Lifestyle Changes & Poor Nutrition
The fast-paced urban lifestyle, coupled with poor dietary habits, has contributed to declining reproductive health. Junk food, pesticide-laden vegetables, and hormone-injected dairy products are wreaking havoc on hormonal balance. Excessive consumption of processed foods high in trans fats and refined sugars can lead to obesity and diabetes, both of which are directly linked to infertility and erectile dysfunction.
2. Pollution & Environmental Factors
India’s severe air and water pollution play a major role in declining fertility rates. Heavy metals, microplastics, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the environment have been linked to lower sperm counts and hormonal imbalances in both men and women. A study published in The Lancet found that sperm counts have fallen by nearly 50% globally in the past few decades, with pollution being a major factor. In India, the presence of arsenic, lead, and industrial waste in drinking water is particularly alarming, as these elements are known to cause reproductive toxicity.
3. Stress & Mental Health Issues
High levels of stress, anxiety, and depression contribute significantly to sexual dysfunction and infertility. Work pressures, financial struggles, and social expectations have left people vulnerable to chronic stress, which increases cortisol levels in the body. High cortisol suppresses testosterone and disrupts ovulation cycles, making conception difficult. Furthermore, mental health stigma in India prevents many from seeking professional help, worsening the problem.
4. Increased Use of Plastics & Chemicals
Daily exposure to plastics, pesticides, and processed foods containing xenoestrogens (chemicals that mimic estrogen) disrupt the body’s natural hormonal balance. Studies have linked plastic usage and chemical exposure to declining sperm count and female infertility. Bisphenol A (BPA), commonly found in plastic containers, has been directly associated with reproductive issues. Moreover, pesticides such as glyphosate used in Indian agriculture have been shown to damage sperm DNA and affect ovulation.
5. Delayed Marriages & Family Planning
With growing career ambitions, late marriages, and delayed family planning have become common in urban India. Fertility declines naturally with age, and by the time many couples decide to conceive, they often struggle due to reduced reproductive capabilities. Women who conceive after the age of 35 face a higher risk of pregnancy complications, including miscarriage and genetic disorders such as Down syndrome. Additionally, men over 40 experience reduced sperm motility and increased chances of sperm DNA fragmentation.
6. Technology & Electromagnetic Radiation
Excessive use of mobile phones, laptops, and Wi-Fi has raised concerns regarding its impact on sperm quality. Studies suggest that electromagnetic radiation from gadgets may contribute to lower sperm motility and viability. Mobile phones kept in pockets or laptops placed on laps for prolonged periods expose reproductive organs to heat and radiation, leading to testicular dysfunction and reduced sperm count.
Delayed Family Planning & Infertility
In India, more couples are choosing to delay marriage and family planning to focus on their careers. While financial stability and career growth are valid concerns, postponing childbearing can lead to serious reproductive challenges. Fertility naturally declines with age, making it harder for couples to conceive later in life. Women who wait until their mid-to-late 30s face a higher risk of complications such as diminished ovarian reserve, irregular ovulation, and an increased chance of miscarriage.
For men, aging affects sperm quality, leading to decreased sperm motility and an increased likelihood of genetic abnormalities in offspring. Experts warn that delayed family planning can contribute significantly to rising infertility rates in India, making it crucial to educate couples about the biological constraints of human fertility. Medical interventions such as fertility treatments and assisted reproductive technologies (ART) may help, but they are expensive and not always successful.
Gender & Infertility: Breaking the Myths
Dr. Sweta Gupta, a leading fertility expert, emphasizes that infertility can affect both men and women equally. In India, however, women are often unfairly blamed for reproductive issues, despite statistics showing that 40% of infertility cases are due to male factors, 40% due to female factors, and 20% due to unknown reasons. This societal stigma places unnecessary emotional and psychological burdens on women, making it harder for couples to seek appropriate medical help.
Dr. Gupta strongly advises couples struggling with infertility to consult a qualified medical professional rather than relying on unscientific treatments or quacks. She warns against seeking help from individuals who lack medical credentials, stating, “If needed, consult a doctor—not a person who builds tents on the roadside.” Addressing infertility requires proper medical diagnosis and treatment, including lifestyle changes, hormonal therapy, and assisted reproductive techniques.
How to Solve This Problem
1. Lifestyle Changes & Healthy Diet
Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can improve reproductive health. Avoiding processed foods, trans fats, and excessive sugar intake can help regulate hormones and maintain a healthy weight.
2. Reducing Stress & Mental Health Support
Practicing mindfulness, meditation, and stress management techniques can help reduce anxiety-related reproductive issues. Seeking therapy or counseling for mental health concerns is also essential for overall well-being.
3. Controlling Pollution & Chemical Exposure
Reducing exposure to plastics, using organic produce, and ensuring clean drinking water can mitigate environmental effects on fertility. Governments should enforce stricter pollution control regulations to protect public health.
4. Encouraging Early Family Planning
Raising awareness about age-related fertility decline and encouraging couples to consider family planning earlier can prevent fertility-related challenges later in life.
5. Regular Health Checkups & Medical Consultations
Routine screenings for hormonal imbalances, diabetes, cardiovascular health, and reproductive function can help diagnose and treat issues early. Consulting certified medical professionals for infertility and ED-related concerns ensures proper treatment.
6. Reducing Porn Addiction & Digital Detox
Limiting pornography consumption, practicing digital detox, and seeking professional help for addiction-related issues can improve sexual health and performance.
7. Promoting Physical Activity & Fitness
Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can boost testosterone levels, improve blood circulation, and enhance overall reproductive health.


